Bitwall CTF Writeup
Introduction
On May 2 to May 4, 2025, we participated in a 3-day Capture the flag competition hosted by BitWall The event featured a wide range of challenges across multiple domains including, ONSIT, Web, Android, Pwn, Forensics, Steganography, Cryptography, Reverse Engineering, Misc. This blog post is a walkthrough of some of the challenges I managed to solve;
Forensics
Silent Supernova 1
To solve this challenge you needed to download the attached zipped ile, which had a file named Kakwa.docs after unzipping.
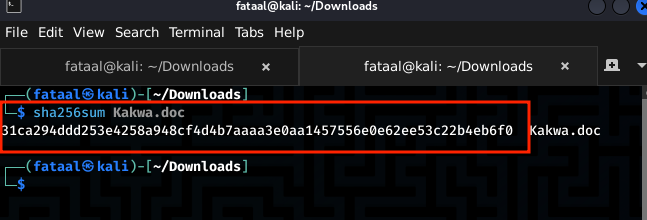
The first question in this category is to get the SHA256 hash of the file, I used sha256sum which is a command-line tool used to calculate and verify SHA-256 cryptographic hashes of files or data. Alternatiely you can use Virustotal for static analysis.
Flag: BitCTF{31ca294ddd253e4258a948cf4d4b7aaaa3e0aa1457556e0e62ee53c22b4eb6f0 }
Silent Supernova 2
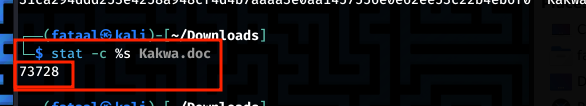
 The second question of this challenge is to get the size of the document in bytes, It was easy to get the size directly on the terminal bu using command
The second question of this challenge is to get the size of the document in bytes, It was easy to get the size directly on the terminal bu using command stat -c %s filenamewhich returns the size of the specified file in bytes using a custom output format.
Flag: BitCTF{73728}
Silent Supernova 3
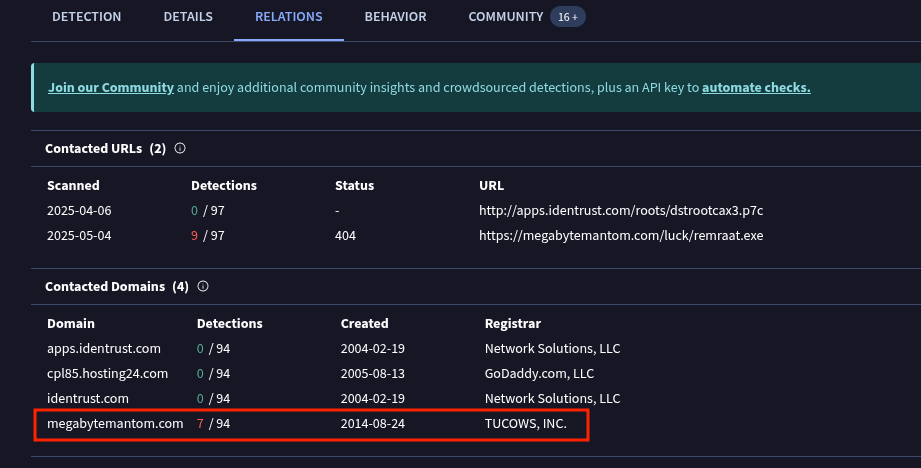
The third question of this challenge was to find the contacted suspicious domain. I used both Any.run and VirusTotal to get the suspicious domain that made the silent DNS Request. On Virustotal you will need to to upload the document for static analysis, on relations tab there is a list of cantacted domains and you will be able to distinguish between the malicious and the legitimate domains based on the number of requests each has.
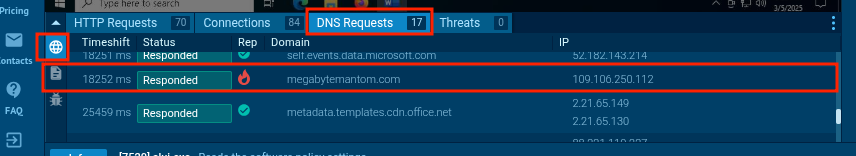
On Any.run you will need to navigate to the network activity panel and then DNS Requests logs tab and manually scroll to see the suspacious domain.
Flag: BitCTF{megabytemantom.com}
Silent Supernova 4
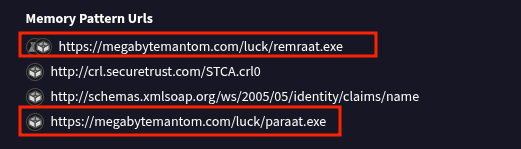
The fourth challenge asked us to identify the auto-executed files. Since the previous question helped reveal a suspicious domain, it’s now easier to trace which files were executed as a result of activity linked to that domain. In Virustotal navigate to behavior tab and check the memory pattern urls section. The files associated with the suspicious domain exhibit clear malware-like behaviour.
Flag: BitCTF{remraat.exe_paraat.exe}
Silent Supernova 5
The fith task of this challenge is to find the malicious function that initiated the malware activity. I used the olevba command line tool that will parse the VBA code and extract all macros from the document, including those that are set to execute automatically when the document is opened. After running olevba on the document I was able to identify the specific function responsible for initiating the malicious behaviour.
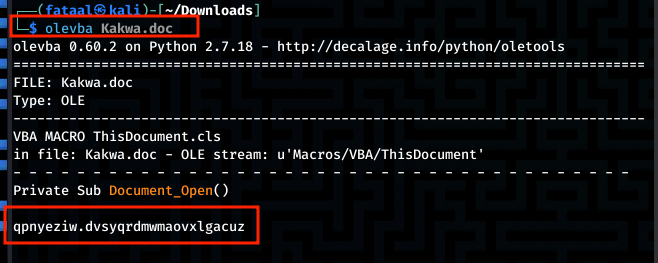 Flag:BitCTF{qpnyeziw.dvsyqrdmwmaovxlgacuz}
Flag:BitCTF{qpnyeziw.dvsyqrdmwmaovxlgacuz}
Silent Supernova 6
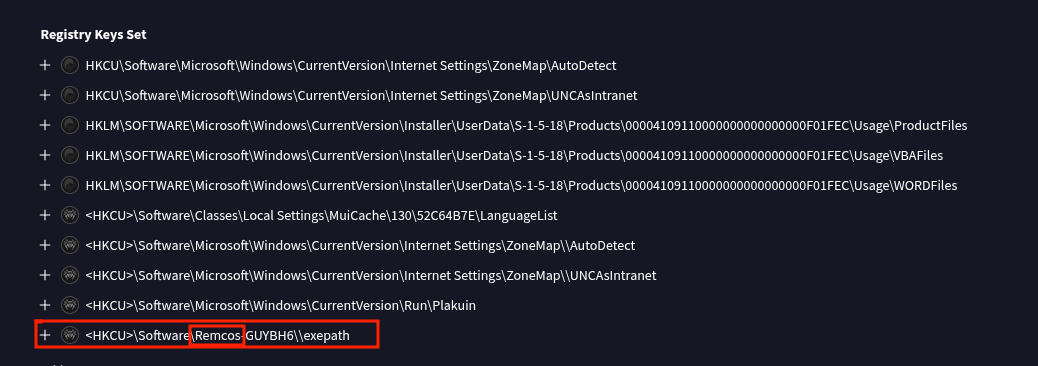
This is the last question of this challenge, you were required to find the specific malware malware associated with the trojan. I tried several things before getting the correct answer for this question. On virustotal static analysis report, there are few things that hinted the Remcos Remote Access Trojan (RAT) point to malicious activity. One of the key signs is the creation of a registry key at HKCU\Software\Remcos-GUYBH6\exepath, which is used to establish persistence by storing the path to the malware’s executable. This registry key ensures that Remcos remains active even after a system reboot.
In addition to registry manipulation, Remcos also involves file activity. A file named logs.dat is both written and dropped on the system, on %APPDATA%\remcos directory. The written aspect could be that the malware generated this file during its execution to store stolen data and the file is created dynamically by the malware while the dropped file could mean that the malware placed this file from an external source or load it from a remote server, making it a critical artifact in the infection chain. Dropped files are often used to expand the attacker’s control over the system, potentially leading to further exploitation.
Another major indicator of Remcos is its use of process injection techniques. The malware injects its malicious code into legitimate Windows processes, this tactic helps it evade detection by security tools. This process injection allows Remcos to operate under trusted system processes, making it more difficult to detect the traces of the malicious activity.
Flag: BitCTF{Remcos}
Misc
Message from Heaven
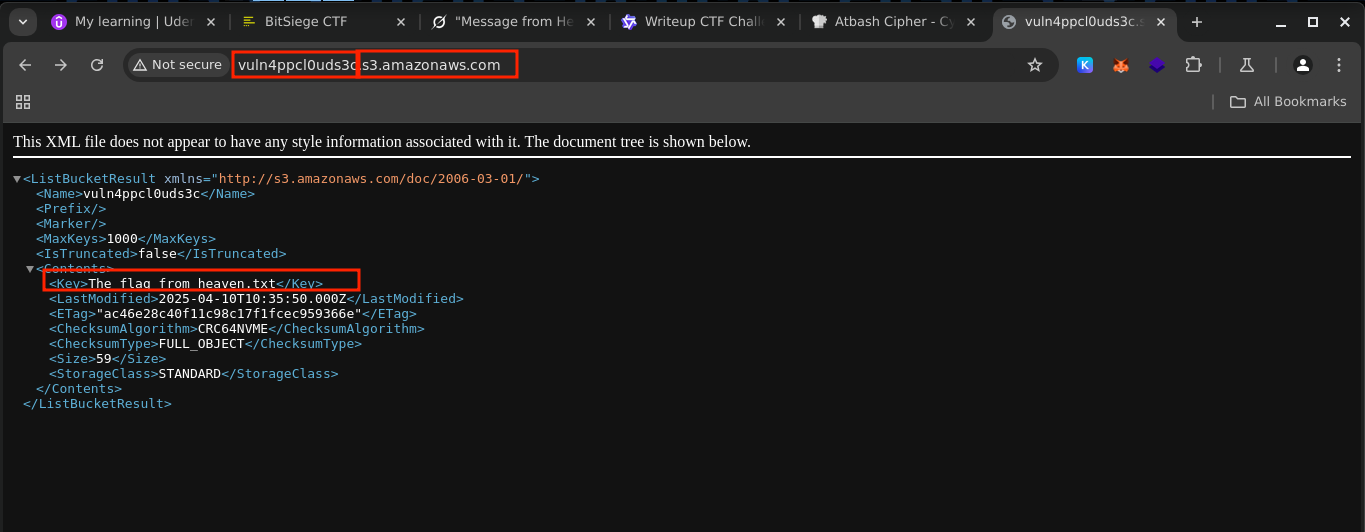
Based on the challenge description the clue was given as vuln4ppcl0uds3c which suggested a cloud security vulnerability with s3c pointing to AWS S3. From my research S3 bucket misconfigurations are a classic where a bucket is left publicly accessible. No direct connection needed hinted that the solution to the challenge is passive. I assumed that the vuln4ppcl0uds3c culd be the bucket name and tried accessing the bucket using, http://vuln4ppcl0uds3c.s3.amazonaws.com/ to check the public access, and if it was public I could see it’s objects fore more clues.
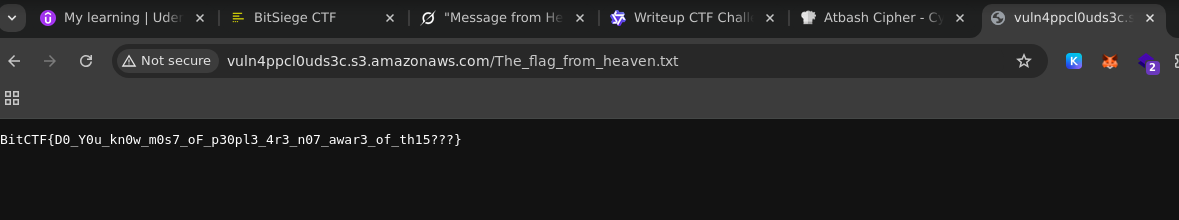
The bucket was accessible and to retrieve the specific file hinted I appended the files name to the endpoint URL on the browser and retrieved the flag
Flag: BitCTF{D0_Y0u_kn0w_m0s7_oF_p30pl3_4r3_n07_awar3_of_th15???}
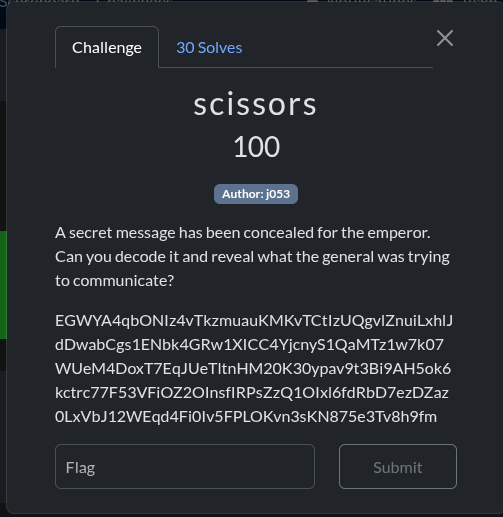
Scissors
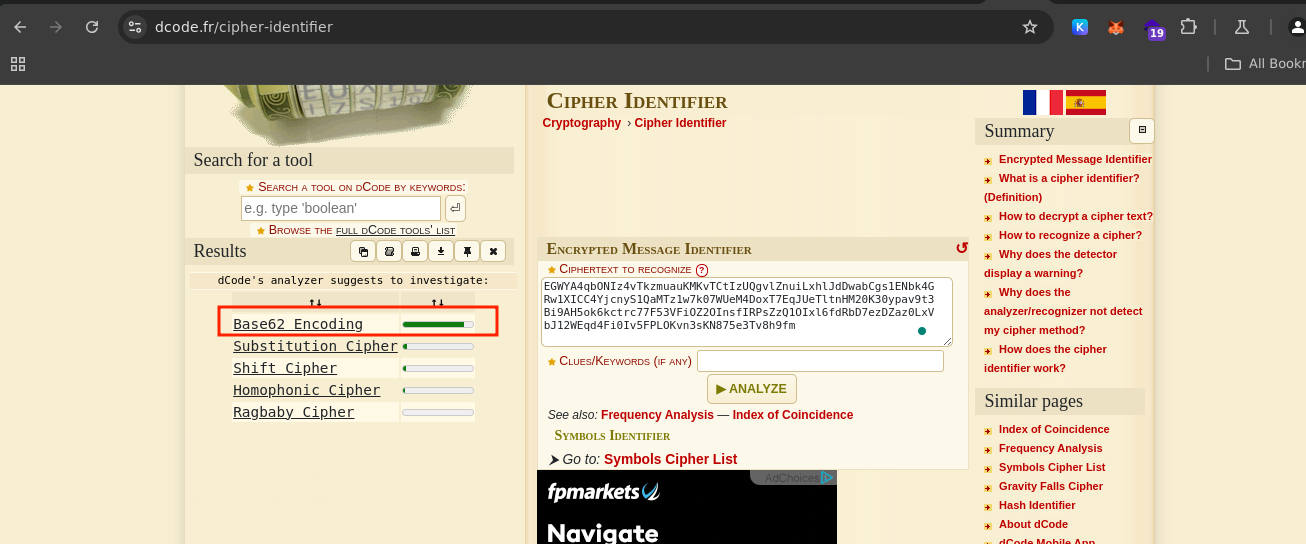
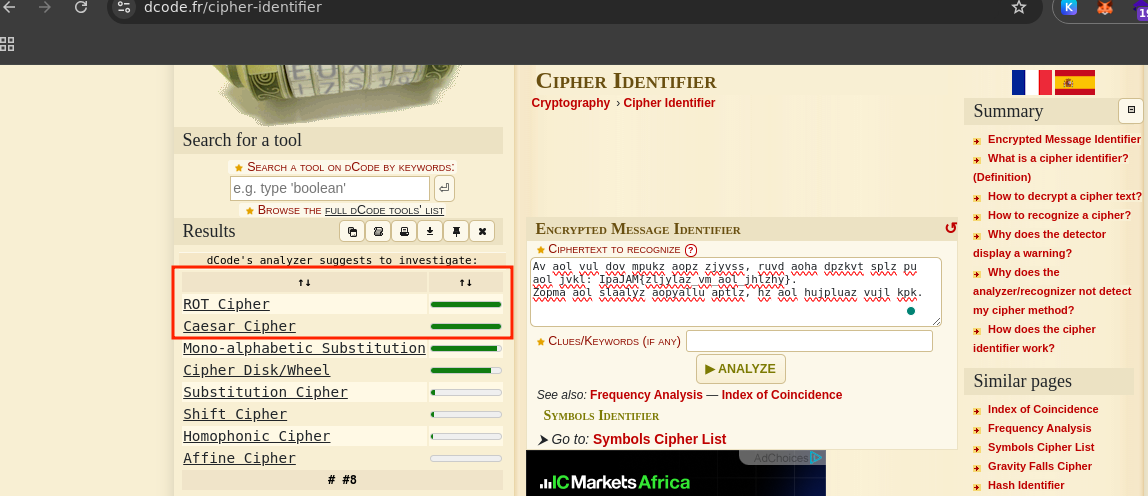
This is a very easy challenge, first I checked to identify the cipher which was Base62 encoding.
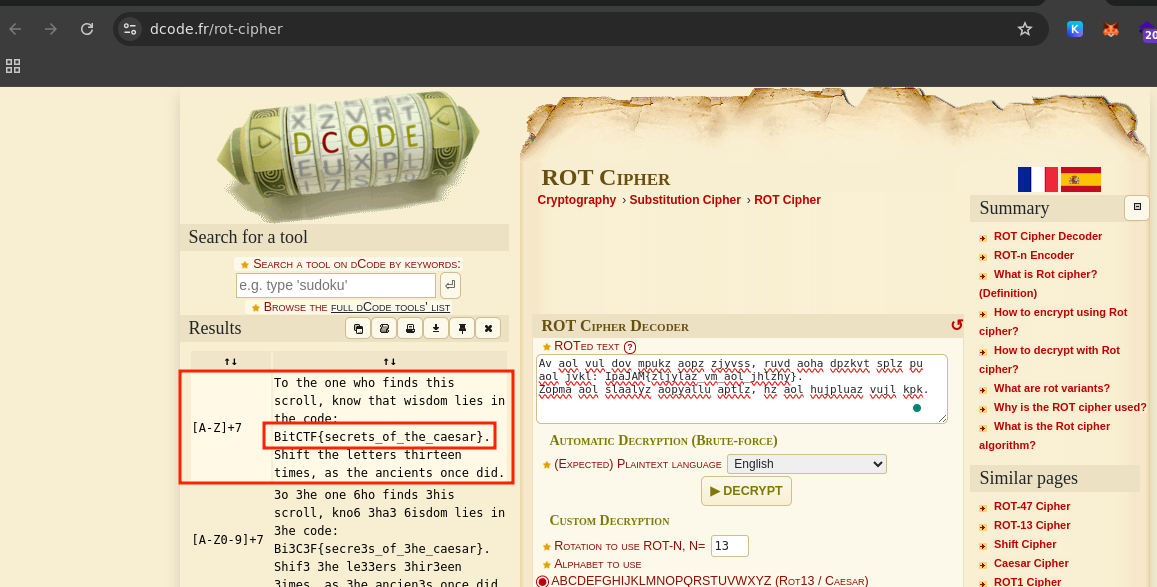
After identifying the cipher I decoded using cyberchef base62 decoding, and checked the decoded cipher again and was identified as ROT Cipher and decoded it using an online tool dcode.fr/rot-cipher to get the flag.
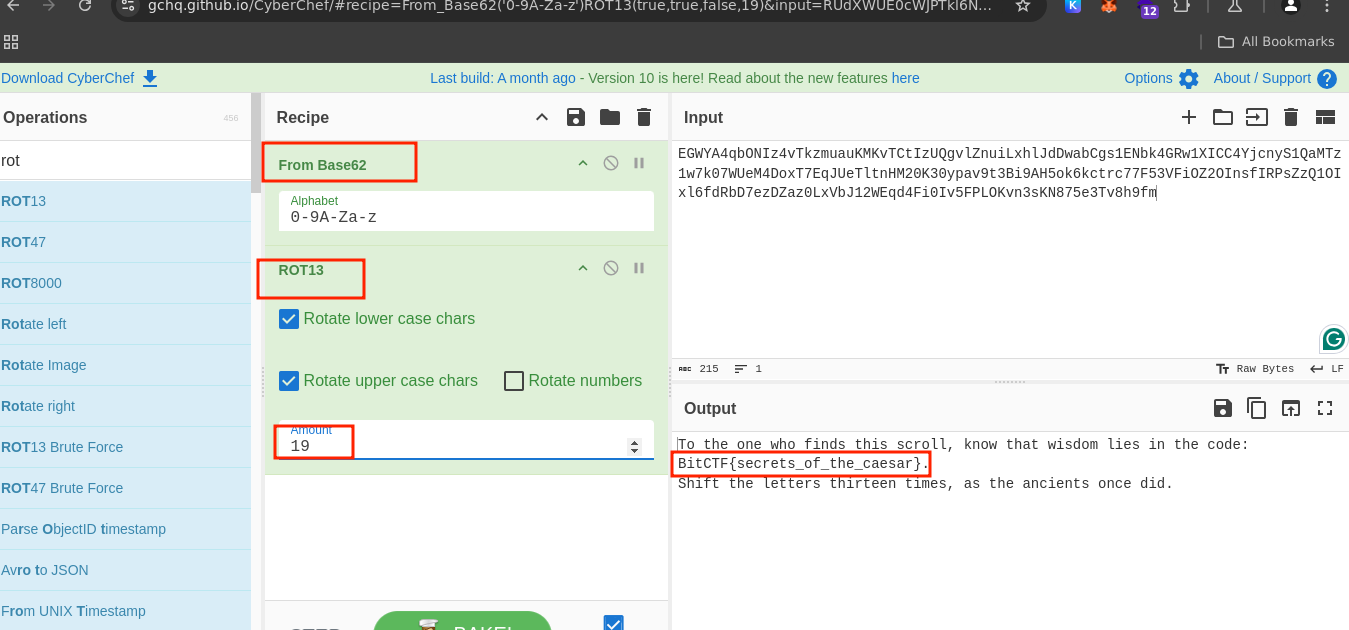
This challenge can also be solved using CyberChef by first decoding the Base62 encoding, followed by applying a ROT cipher with a 19-shift decryption.
Flag: BitCTF{secrets_of_the_caesar}
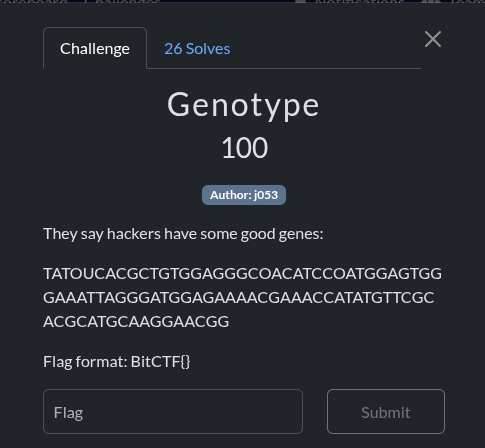
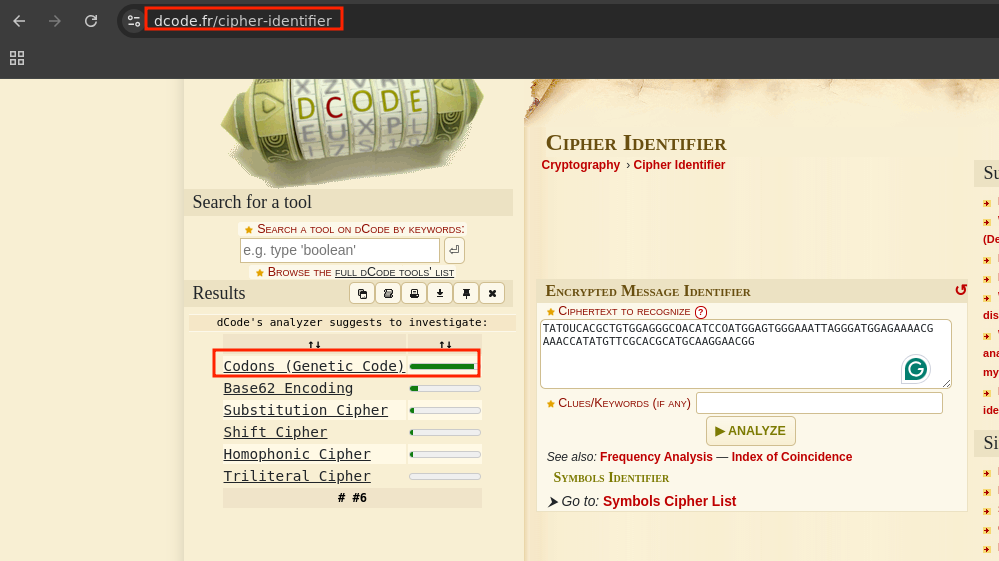
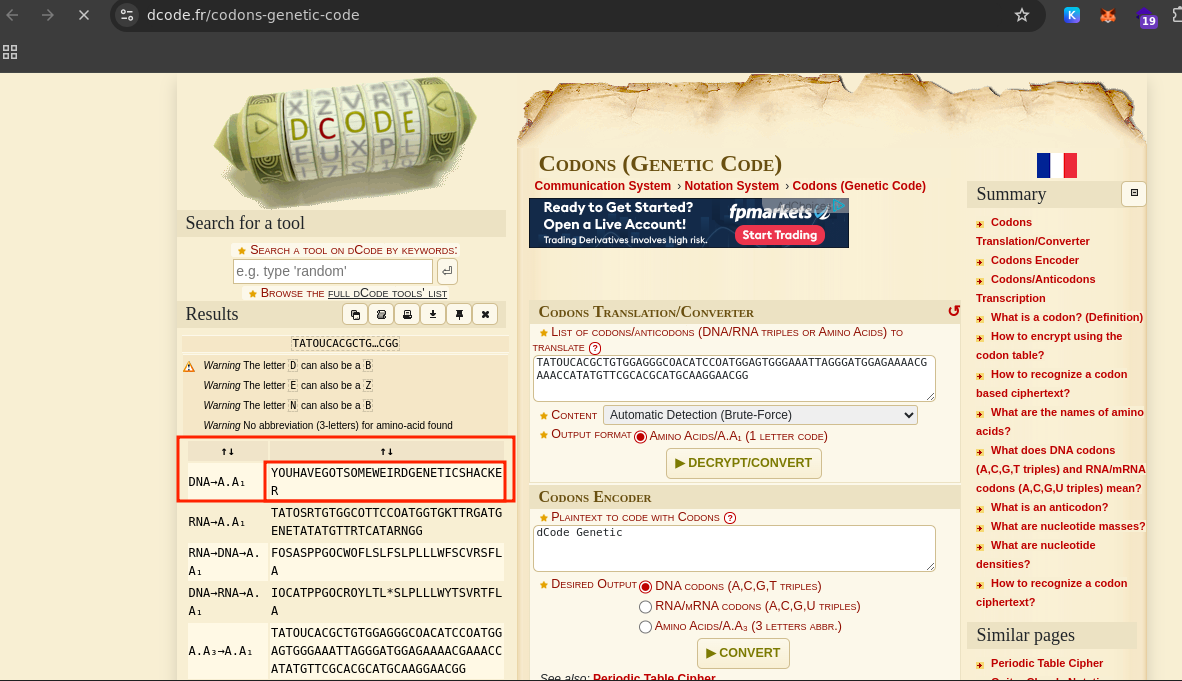
Genotype
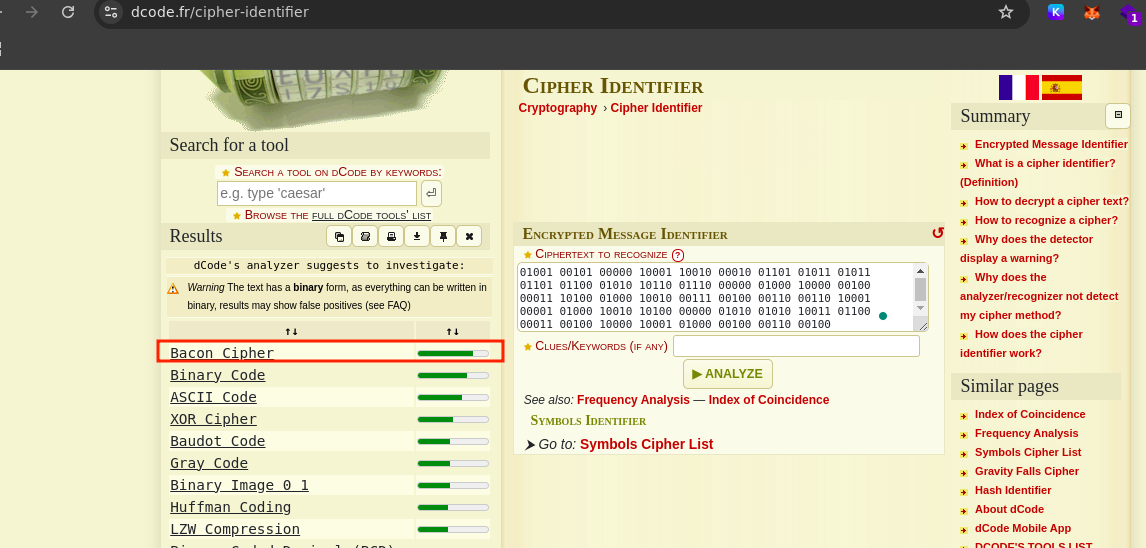
I used dCode’s Cipher Identifier to analyze the string, and it identified the encoding as Codons (Genetic Code), which is a DNA-based cipher. I then decoded the string using the Codons decoder available at dcode
Flag: BitWall{YOUHAVEGOTSOMEWEIRDGENETICSHACKER}
I hope you are loving the challenges
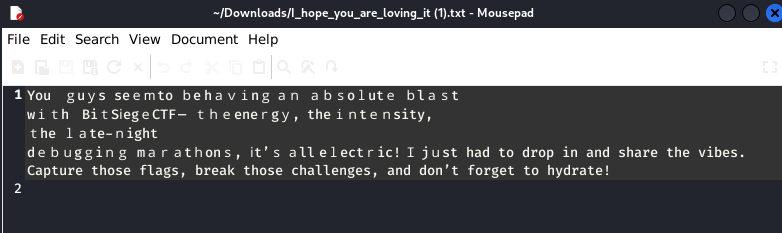
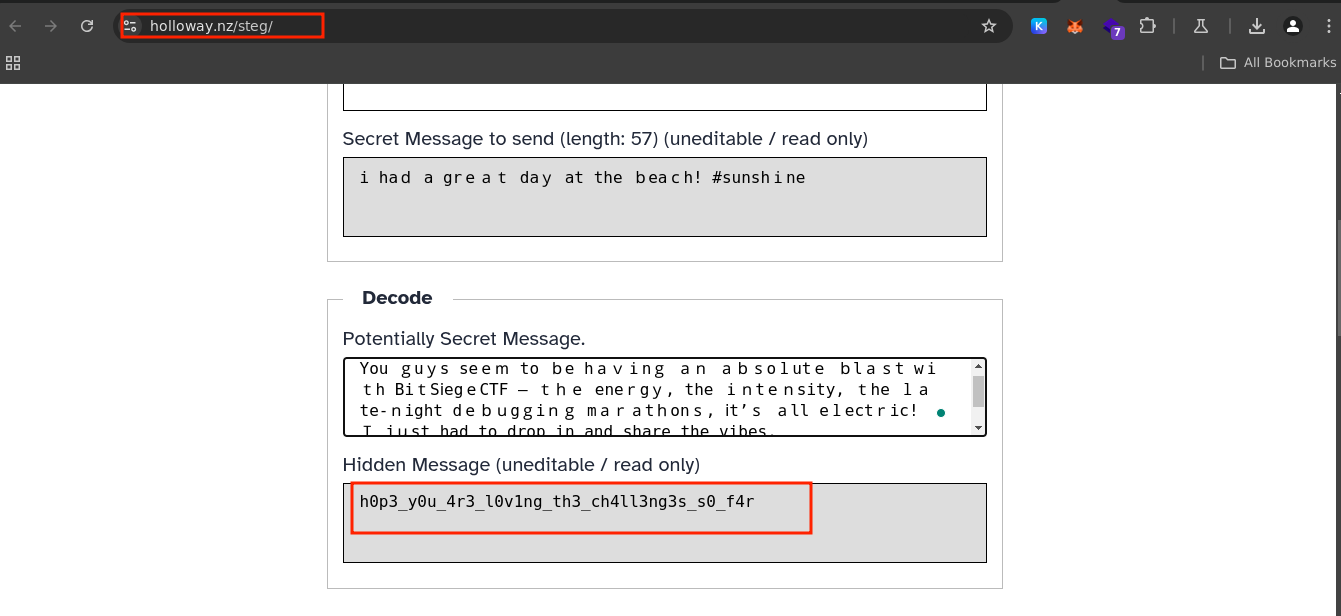
This was a very easy challenge, you were required to download the attached txt file, find the hidden message from the encoded text, I used the online tool Holloway to decode the obfuscated text
Flag: BitCTF{h0p3_y0u_4r3_l0v1ng_th3_ch4ll3ng3s_s0_f4r}
Cryptography
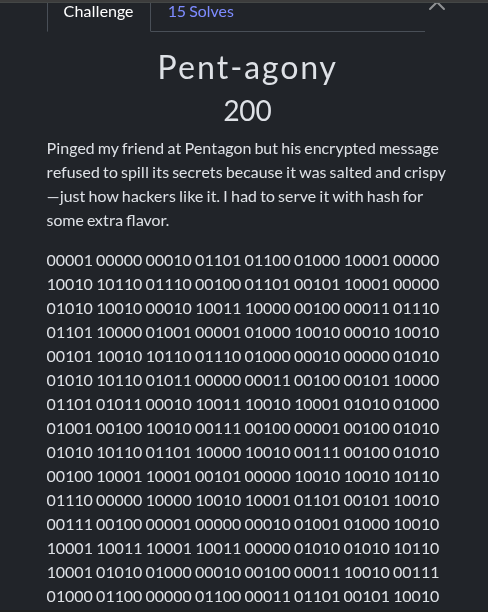
Pent-agony
1
2
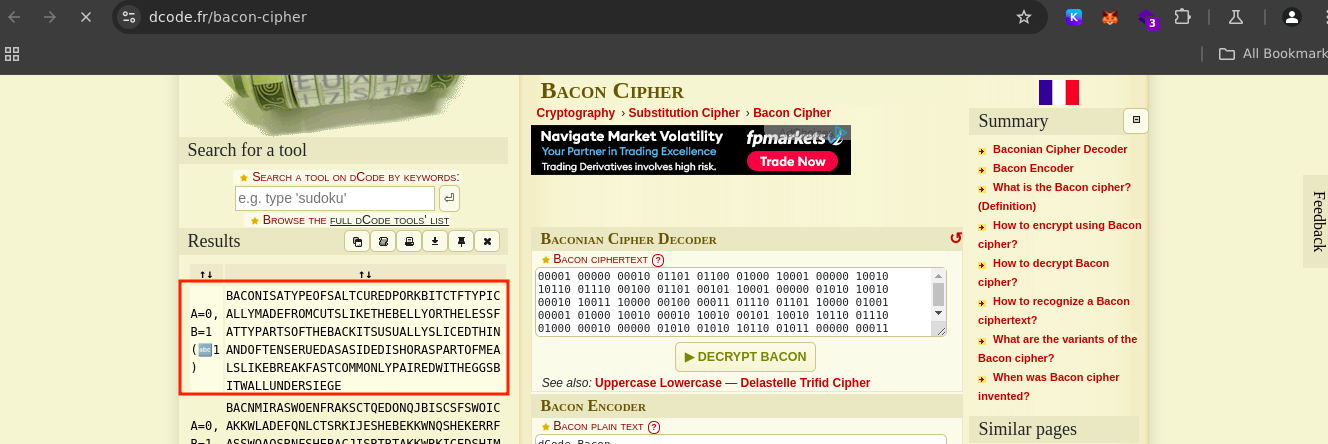
"Bacon is a type of salt-cured pork, typically made from cuts like the belly or the less fatty parts of the back. It’s usually sliced thin and often served as a side dish or as part of meals like breakfast, commonly paired with eggs. Bitwall under siege."
Flag: BitCTF{Bitwall_Under_Siege}
Steganography
More categories and posts coming soon